How many types of motherboards available and how do they differ from each other?
Motherboards come in various types, each designed to fit specific types of processors, form factors, and functionalities. Some of the common types of motherboards include:
- ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended): ATX is the most common form factor for desktop PCs. These motherboards typically offer a wide range of features and expansion slots, making them suitable for gaming, productivity, and general use.
- Micro ATX: Micro ATX motherboards are smaller than ATX boards but still offer decent expansion options. They are a good choice for smaller desktop PCs where space is a concern.
- Mini-ITX: Mini-ITX motherboards are even smaller than Micro ATX boards and are designed for compact builds, such as home theater PCs (HTPCs) or small form factor gaming rigs. They usually have fewer expansion slots but are highly efficient in space-constrained environments.
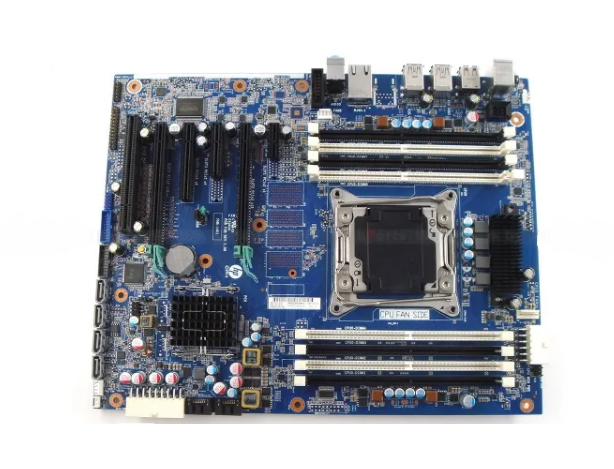
- Extended ATX (E-ATX): E-ATX motherboards are larger than standard ATX boards and offer additional expansion slots and features. They are often used in high-end gaming PCs and workstations that require multiple GPUs, storage devices, and other peripherals.
- ITX (Information Technology eXtended): ITX motherboards come in different sizes, including Mini-ITX and Nano-ITX. They are designed for specific applications where space is extremely limited, such as embedded systems and small form factor PCs.
- Server Motherboards: These motherboards are designed for use in servers and data centers. They often support multiple processors, large amounts of RAM, and additional features such as remote management capabilities.
- Workstation Motherboards: Workstation motherboards are similar to server motherboards but are tailored for professional workstations used in tasks such as CAD/CAM, 3D rendering, and content creation. They offer high performance, stability, and support for specialized hardware.
- Gaming Motherboards: Gaming motherboards are optimized for gaming performance and often come with features such as enhanced audio, overclocking capabilities, and RGB lighting. They are typically available in ATX and Micro ATX form factors.
These different types of motherboards differ in terms of size, form factor, features, expansion options, and compatibility with processors and other hardware components. When choosing a motherboard, it’s important to consider factors such as the intended use of the system, available space, budget, and compatibility with other components.