Can you explain how a motherboard communicates with the different hardware components of a computer system
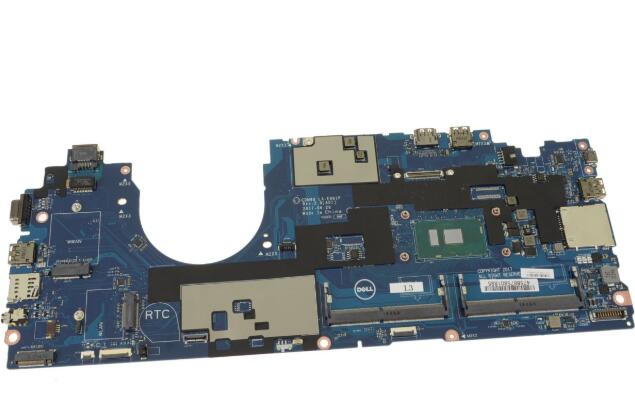
The motherboard serves as the main circuit board of a computer system and facilitates communication between various hardware components. Here’s how the motherboard communicates with different components:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit):
- The CPU is the central processing unit of the computer and executes instructions stored in memory.
- The motherboard provides a socket for the CPU to be installed and connects it to the rest of the system via the system bus.
- The chipset on the motherboard manages data flow between the CPU, memory, and other peripherals.
- RAM (Random Access Memory):
- RAM is the primary memory of the computer system where data and instructions are temporarily stored for quick access by the CPU.
- The motherboard contains memory slots (DIMM slots) where RAM modules are installed.
- The memory controller, part of the chipset on the motherboard, manages data transfer between the CPU and RAM.
- Storage Devices (Hard Drives, Solid-State Drives):
- Storage devices such as hard drives and solid-state drives are connected to the motherboard via SATA (Serial ATA) or NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) interfaces.
- The motherboard provides SATA or M.2 connectors for connecting storage devices, allowing data transfer between the CPU and storage.
- Expansion Cards (Graphics Cards, Network Interface Cards):
- Expansion cards, such as graphics cards and network interface cards (NICs), are installed in PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots on the motherboard.
- The motherboard provides PCIe lanes for data transfer between the CPU and expansion cards.
- The chipset manages communication between the CPU and PCIe devices and assigns resources to each expansion card.
- Peripherals (USB Devices, Audio Devices):
- Peripherals such as USB devices, keyboards, mice, and audio devices are connected to the motherboard via USB ports, audio jacks, and other connectors.
- The motherboard provides controllers and interfaces for connecting peripherals, allowing data transfer and communication with the CPU.
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System):
- The BIOS is firmware stored on a chip on the motherboard and initializes hardware components during the boot process.
- The motherboard communicates with the BIOS to retrieve configuration settings and boot instructions, enabling the system to start up and load the operating system.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU):
- The power supply unit (PSU) supplies electrical power to the motherboard and other components of the computer system.
- The motherboard distributes power from the PSU to various hardware components, ensuring proper voltage levels and power delivery.
Overall, the motherboard plays a central role in facilitating communication and data transfer between different hardware components of a computer system, enabling them to work together seamlessly to perform various tasks and functions.